- Saturday, 14 March 2026
Kathmandu-Tarai Expressway achieves 39% physical progress
By Anil Parajuli,Hetauda, Apr. 30: The Kathmandu–Tarai–Madhes Fast Track (Expressway), a National Pride Project of Nepal, is progressing under the supervision of the Nepali Army. As of mid-April 2025, the project has achieved 39.34 per cent physical progress and 41.06 per cent financial progress, according to Nepali Army Spokesperson and Brigadier General Gaurav Kumar KC.
Of the 13 construction packages under the project’s master plan, packages from 1 to 10, including sub-packages 8a, 8b, 9a, and 9b, are currently under construction or the implementation phase. However, land acquisition challenges in the Khokana–Bungamati segment under package 11 have delayed the procurement process. Compensation coordination with stakeholders is ongoing in this segment, said KC.
In efforts to resolve the land acquisition delays, alternative design options are being explored. On April 1, 2025, 10-0-0-1.06 ropani of land from the Bosi Khanki Guthi in Bungamati was acquired by the Ministry of Physical Infrastructure and Transport for the project. An additional 178-9-0-1.75 ropani of land remains to be acquired in the Khokana–Bungamati area, with further valuation pending for 165-6-0-3 ropani.
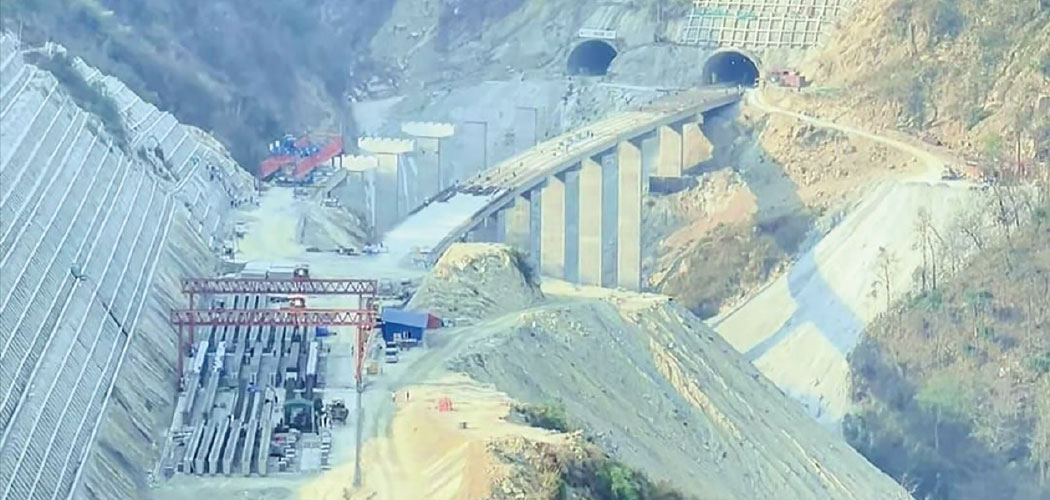
The Expressway includes seven tunnels, with a total length of approximately 10.979 kilometres. In tunnel package 1, the 3,355-metre Mahadevtar Tunnel has seen a significant progress: 2,029 metres (61%) of the right tunnel and 2,286 metres (68%) of the 3,386-metre left tunnel have been excavated. Meanwhile, breakthroughs have been achieved in the 1,691-metre Dhedre Tunnel (package 2) and the 1,623-metre Len Danda Tunnel (package 3).
According to the Army Headquarters, construction is underway on the Devi Chaur Tunnel (1,000 metres) and the Sisautar Tunnel (390 meters) following completion of procurement and design processes.
The 2,250-metre Chandram Bhir Tunnel has achieved 91.03 metres of progress, while design work is about to begin for the 583-metre Mauri Bhir Tunnel, approved by the Cabinet on November 10, 2024.
Out of 89 planned bridges, procurement contracts have been signed for 85, and most of them are currently under construction. Foundations have been completed for many bridges, with superstructure work ongoing. So far, five bridges have been completed, with a target to finish an additional 20 within this fiscal year.
Land acquisition has been completed for the 24.8 to 70.977 km section, and construction is underway. Additional approvals are in process for acquiring 128-2-0-2.55 ropani of land in Kathmandu, 54-11-3-1.82 ropani in Lalitpur for tunnel construction, and 28-15-3-1.19 ropani in Makwanpur.
To date, 44,420 trees of various species have been felled for the project. In compensation, 705,552 saplings have been planted. Supplementary Environmental Impact Assessments (EIAs) have been approved for additional land and vegetation removal resulting from route realignments and design changes.
The Ministry of Forest and Environment approved supplementary EIAs for the Mahadevtar–Dhedre–Len Danda and Rajdamar–Baghdev–Nijgadh sections in December 2023. Consequently, tree felling has been carried out in coordination with relevant forest offices.
Additionally, the Cabinet, on September 5, 2024, approved the use of 51.871 hectares of national forest land across several localities in Makwanpur district for expressway construction, including the clearance of 27,748 trees. Of these, 12,470 trees have already been cut down.
The EIA for the Makkhubesi–Devi Chaur–Sisaotar–Sisneri–Mahadevtar section (6.5 to 24 km) is currently under review by the Ministry of Forests and Environment.
Meanwhile, construction continues on sub-base layers, bioengineering works, retaining walls, and service roads.
Spanning 70.977 kilometres from Khokana to Nijgadh, construction of the expressway was entrusted to the Nepali Army in 2017 by then Prime Minister Pushpa Kamal Dahal ‘Prachanda’ with a four-year completion target. Originally estimated at Rs. 175 billion, the project cost has since risen to Rs. 211.93 billion.
For the fiscal year 2024/25, a budget of Rs. 22.55 billion was allocated, of which Rs. 8.07 billion has been spent as of mid-April, 2025.



-original-thumb.jpg)

-square-thumb.jpg)