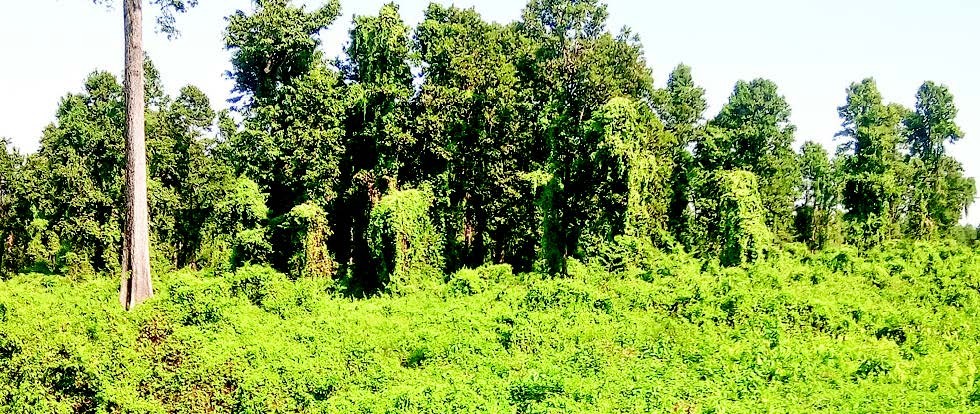
Jalthal, Nepal's richest forest in biodiversity

By Our Correspondent
Jalthal, Nov. 22: A research carried out jointly by the Forest Division Office, Jhapa, Forest Action Nepal and the Community Forest Consumer's Federation's Unit has revealed that the forest located at Jalthal, east-south in Jhapa district, hosts maximum biodiversity in Nepal.
The research showed that the diverse range of floras, which usually grow in higher hilly and the Terai regions were found in the forest.
The forest area, commonly known as Jalthalban, spreads in Haldibari, Kachankawal, Barhadashi Rural Municipalities and Bhadrapur Municipality in southern Jhapa.
Bishnu Lal Ghimire, Chief, Forest Division Office, Jhapa said, "Plants which usually grow in high hilly region such as Kattus, Thakal, Saj, Khanyu, Fadir, Kyamuna and Latahar are found in this forest."
Floras such Sal, Khayar, Simal, Saj, Bhalayo, Thatiwan, Bohori and Kutmiro, which usually grow in the Terai region are also found in the forest, he added.
Along with floras, the forest also hosts a diverse range of faunas. "Faunas such as wild elephants, deer, wild boar, peacock, Salak, python, tortoise, Thotari and porcupine are widespread in the forest," said Ghimire.
The forest has also been a home to extinct species of birds and insects. Jalthalban is the only forest in Nepal which hosts such diverse biodiversity, said Ghimire.
The geographical feature of the forest is the major whys and wherefores behind the availability of a wide range of biodiversity.
From lands of inner Terai to high hills in the Mawan area of the forest, the forest incorporates both the Terai and hilly regions.
"The high hills of Mawan area, situated within the forest have made the floras and faunas of both Terai and hilly regions available," said Lilanath Sharma, facilitator, Forest Action Nepal.
We have started our research on biodiversity from this year, said Sharma.
Since Sal trees are found in huge number in the forest, it has made the co-existence of flora and faunas possible. According to Ghimire, the Sal trees make it easier for other floras to grow.
Sal trees even allow other floras to grow in its barks and branches.
"Our latest research showed that 32 species of floras grow in Sal trees within one metre square," said Ghimire. Experts also suggest for conservation of floras for the conservation of biodiversity on the whole.
Jalthalban forest has 22 community forests. The forest has occupied 44.21 km land in 6,260 hectares.
Recent News

Do not make expressions casting dout on election: EC
14 Apr, 2022
CM Bhatta says may New Year 2079 BS inspire positive thinking
14 Apr, 2022
Three new cases, 44 recoveries in 24 hours
14 Apr, 2022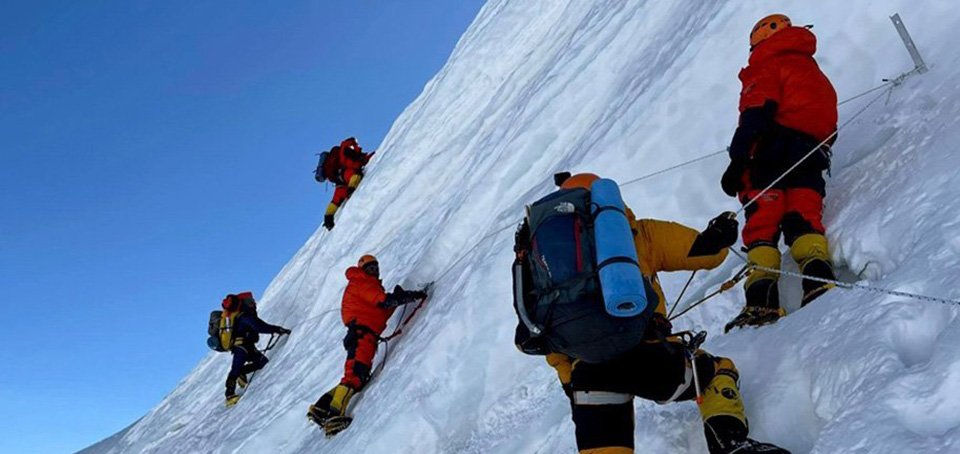
689 climbers of 84 teams so far acquire permits for climbing various peaks this spring season
14 Apr, 2022
How the rising cost of living crisis is impacting Nepal
14 Apr, 2022
US military confirms an interstellar meteor collided with Earth
14 Apr, 2022
Valneva Covid vaccine approved for use in UK
14 Apr, 2022
Chair Prachanda highlights need of unity among Maoist, Communist forces
14 Apr, 2022
Ranbir Kapoor and Alia Bhatt: Bollywood toasts star couple on wedding
14 Apr, 2022
President Bhandari confers decorations (Photo Feature)
14 Apr, 2022